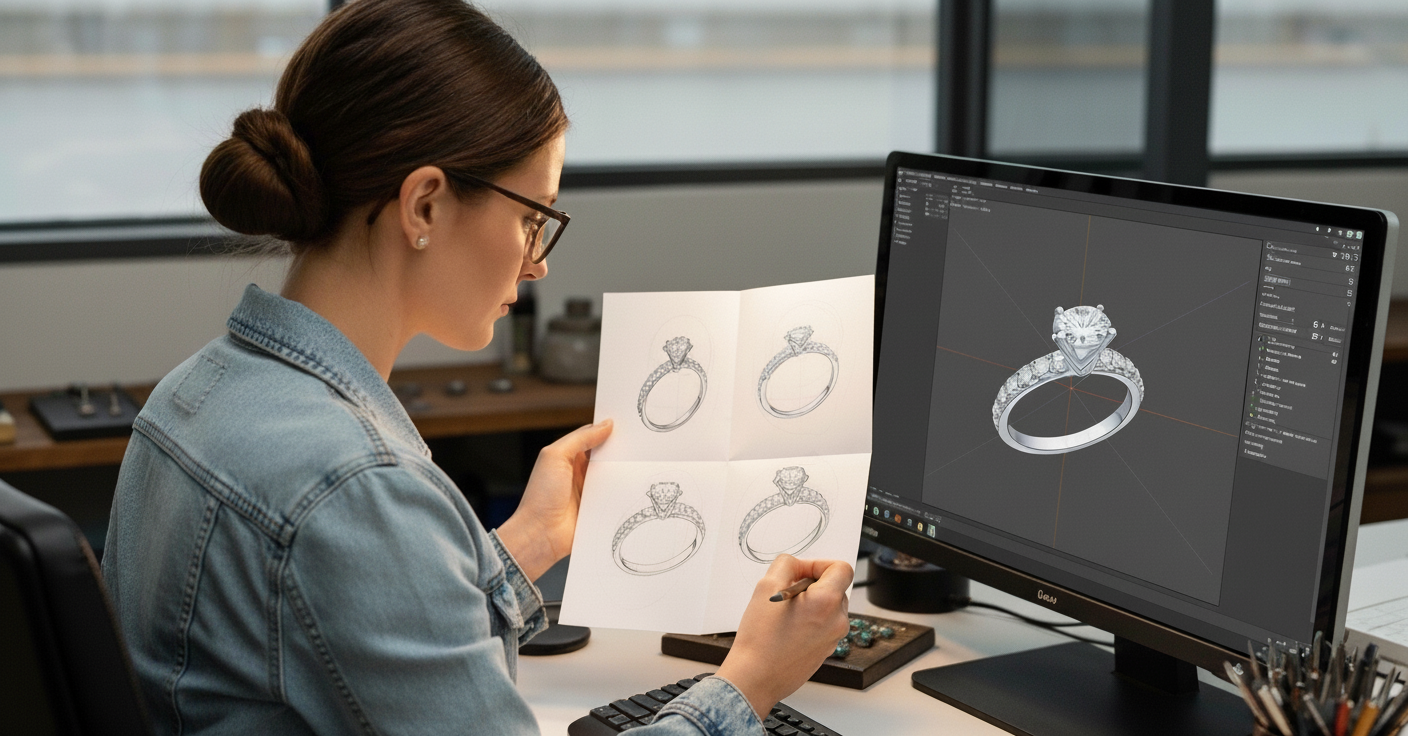
CAD vs. Traditional Sketching: Which Is Better for Jewelry?
Designing custom jewelry today often blends the best of two worlds: the timeless artistry of hand sketching and the modern precision of Computer-Aided Design (CAD). A quick sketch can capture the first spark of inspiration; it works best for aesthetic representation of a custom product, while CAD jewelry design takes that vision and transforms it into a detailed, production-ready model. Neither approach is strictly better; each has unique strengths, and together they create a powerful design process.
In this article, we’ll get through everything you need to know about how hand sketching and CAD differ, where each method shines, how they complement one another, and ultimately, which approach might be best for your custom jewelry journey.
What is Traditional Sketching in Jewelry?
In simple words, we call it jewellery design drawings or jewelry sketching. Traditional sketching is the art of drawing a jewelry design by hand. With expertise, patience, and using tools like a pencil, gouache, watercolor, and paper, a designer can quickly capture the essence of an idea. This is one of the oldest and most direct traditional methods, allowing for a personal touch and artistic expression from the very beginning of the design process.
These manual drafting techniques emphasize creativity and concept exploration over technical accuracy. A sketch can show storyline, concept, emotion, and imagination all at once. And when done exceptionally well, it transforms a piece of jewelry from being just another product into something far more meaningful, a story the buyer can see themselves in. That’s what makes sketched designs so powerful: they create a connection, turning jewelry into something unforgettable. It’s the first step where a vision begins to take shape before moving to more detailed stages. In the following sections, we will explore how jewelers use these sketches and the skills involved.
How do jewelers create designs using manual sketches?
Jewelers begin the product design process by translating their ideas onto paper. With manual drafting techniques, they can freely experiment with shapes, lines, and forms without the constraints of software. This hands-on approach allows them to quickly visualize multiple concepts and capture a design’s unique feel.
The main difference between this method and digital design is its immediacy. Traditional methods are about exploration and artistry. While there is a higher chance of human error in measurements, the goal at this stage is to establish the overall aesthetic and communicate a creative vision effectively.
Unlike the rigid precision of computer-based tools, a hand-drawn sketch conveys a personal touch that can be very appealing to clients. It’s a powerful communication tool that brings an idea to life in a way that feels organic and connected to the artist’s hand before any technical refinement begins.
What skills are involved in traditional sketching?
Traditional sketching requires a blend of artistic talent and technical understanding. While anyone can pick up a pencil, creating a professional jewelry sketch involves specific abilities. The learning curve is often more intuitive than learning complex CAD software, as it builds on natural drawing abilities rather than technical commands.
A designer must have a strong sense of proportion, perspective, and an eye for detail. They need to understand how light interacts with different materials and gemstones to make the sketch look realistic. This part of the design process is fundamental for creating a compelling visual.
Key skills involved include:
- Artistic Vision: The ability to translate an abstract idea into a visual form.
- Understanding of Form: Knowing how a 2D drawing will translate into a 3D object.
- Shading and Rendering: Creating depth and realism to showcase materials and textures.
- Perspective Drawing: Accurately representing the jewelry from different angles.
What are the benefits and limitations of traditional sketching?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Why it shines | Creative Freedom – Sketching lets your ideas flow without any software restrictions. You can explore shapes, textures, and styles freely. Rapid Ideation – Capture your initial thoughts instantly before they slip away. Perfect for brainstorming multiple concepts quickly. Personal Touch – Each sketch reflects the designer’s hand and personality, creating an emotional story that resonates with clients. Simple & Accessible – All you need is a pencil and paper: no expensive tools or technical knowledge required. |
| Challenges | Lack of Precision – Achieving symmetry, measurements, and technical accuracy is more challenging. Editing Takes Time – Making big changes often means redrawing the design. Limited Scalability – Hard to replicate designs consistently or prepare for large-scale production. Sharing & Collaboration – Physical sketches are harder to share instantly or work on collaboratively. |
| Best Use | Ideal for early concept development, free-flowing creativity, brainstorming, and designs where emotional storytelling and artistic expression are prioritized. |
What is CAD (Computer-Aided Design) in Jewelry?
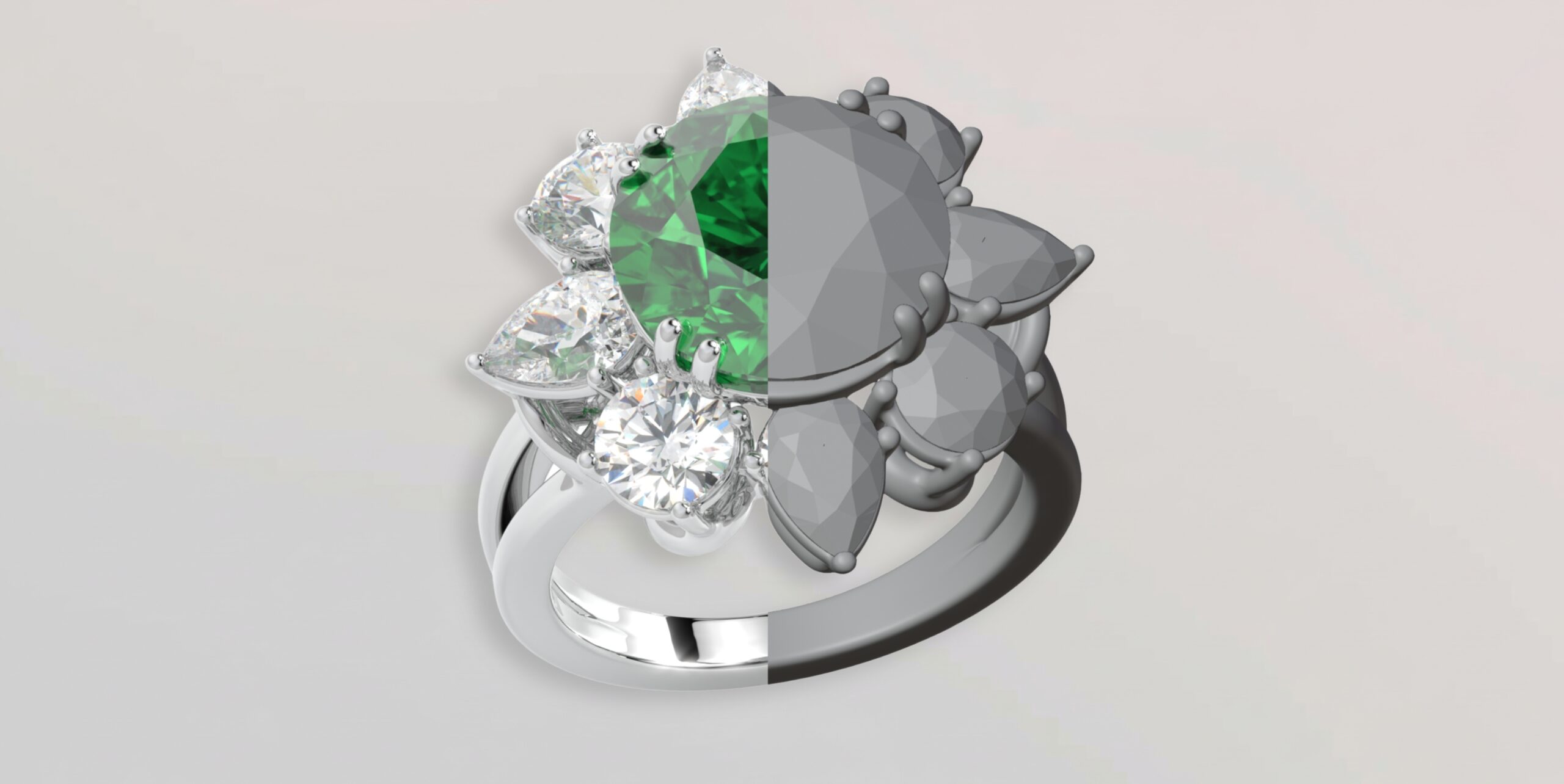

CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, involves using specialized software like MatrixGold, RhinoArtisan to create highly detailed and precise 2D or 3D models of jewelry. This technology has revolutionized the product design industry by introducing a level of accuracy that is nearly impossible to achieve by hand. It has become an essential part of the jewelry production process.
With CAD software, you can build a virtual prototype of your jewelry piece, allowing you to see it from every angle before it’s made. This digital approach ensures every measurement is exact, which is vital for stone setting and manufacturing. Let’s look at the specific tools used and how they work.
What tools and software are commonly used in CAD?
Jewelry designers use a variety of CAD software programs, each offering powerful features for creating intricate designs. These digital tools are the best tools for achieving perfect precision, allowing you to define exact measurements, align elements flawlessly, and create complex geometric shapes with ease.
Professionals often prefer CAD over manual drawing today because it streamlines the manufacturing process. A CAD file can be used directly with 3D printers or CNC machines to create a wax model or the final piece, ensuring the design is produced exactly as intended. This integration removes guesswork and reduces errors.
Common CAD software that Most of the artists used:
Rather than matrixGold, RhinoArtisan, and Yewelry Dream, which are commonly used but there are also other tools and software are there that people use to create a CAD. Here are the following;
Jewelry Design Software Comparison
| Software | Organic Modeling | Parametric Design | Jewelry-Specific Tools | User Experience (UX) | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Design | Moderate – Good for artistic shapes | Basic – Limited control | Excellent – Tailored for jewelry | Intuitive and polished | Highly flexible |
| Blender | Strong – Great for sculpting and organic art | Very limited | Not jewelry-focused | Moderate | Basic |
| Firestorm | Decent – Allows flowing forms | Moderate | Excellent – Suited for jewelry making | Easy to learn | Highly flexible |
| Fusion 360 | Weak for organic shapes | Strong – Precision engineering | Not jewelry-oriented | Smooth workflow | Moderate |
| JewelCAD (JCD) | Moderate | Excellent – Smart parametric control | Excellent – Made for jewelers | Average interface | Very flexible |
| Maya | Excellent – Ideal for freeform modeling | Weak | Not jewelry-specific | Complex for beginners | Limited |
| Modo | Strong – Smooth organic modeling | Weak | Not jewelry-specific | User-friendly | Moderate |
| Rhinoceros (Rhino) | Strong – Great balance | Strong – Good parametric features | Moderate – needs plugins | Slightly technical | Moderate |
| SolidWorks | Weak – Geometric focus | Excellent – Engineering-grade precision | Not jewelry-specific | Professional-grade | Moderate |
| TinkerCAD | Very weak | Very basic | Not suited for jewelry | Extremely beginner-friendly | Minimal |
How does CAD work for jewelry designers?
For jewelry designers, the CAD design process begins with creating a digital 3D model on a computer. Using a mouse or digital pen, they build the piece component by component, from the band to the prongs holding the stone. This digital environment allows for incredible control over every detail of the product design.
One of the greatest strengths of CAD is the ability to make modifications effortlessly. A designer can adjust the size of a band, change a stone’s shape, or experiment with different settings with just a few clicks. This dramatically improves the speed of the design process compared to redrawing a sketch by hand.
This ability to iterate quickly and visualize the piece in 3D answers an important question: yes, CAD absolutely improves the accuracy and speed of design projects. It allows designers to perfect their creations and catch potential issues before the expensive manufacturing stage even begins.
What are the benefits and challenges of CAD in jewelry design?
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Why it shines | Precision & Accuracy – Every line, curve, and measurement is exact, making it production-ready. Speed & Efficiency – Tasks like scaling, duplication, labeling, and adjustments happen in seconds. Easy Editing – Changes can be made quickly without starting over. 3D Visualization – See designs in realistic 3D to help clients and teams visualize the final piece. Collaboration Made Easy – Share files instantly with clients, team members, or manufacturers, even across locations. Direct Manufacturing Integration – CAD files plug straight into 3D printing, prototyping, and casting workflows. |
| Challenges | Cost – Professional CAD software and hardware can be expensive. Learning Curve – Mastering CAD takes time, training, and practice. Technical Reliance – Designs depend on computers and software; crashes or data loss can happen. Creativity Trap – Overuse of digital libraries may limit originality if designers rely too heavily on pre-made elements. |
| Best Use | Ideal for refining designs, preparing technical drawings, creating complex projects, producing 3D visualizations, and ensuring designs are ready for manufacturing. |
CAD vs. Traditional Sketching Jewelry: Head-to-Head Comparison
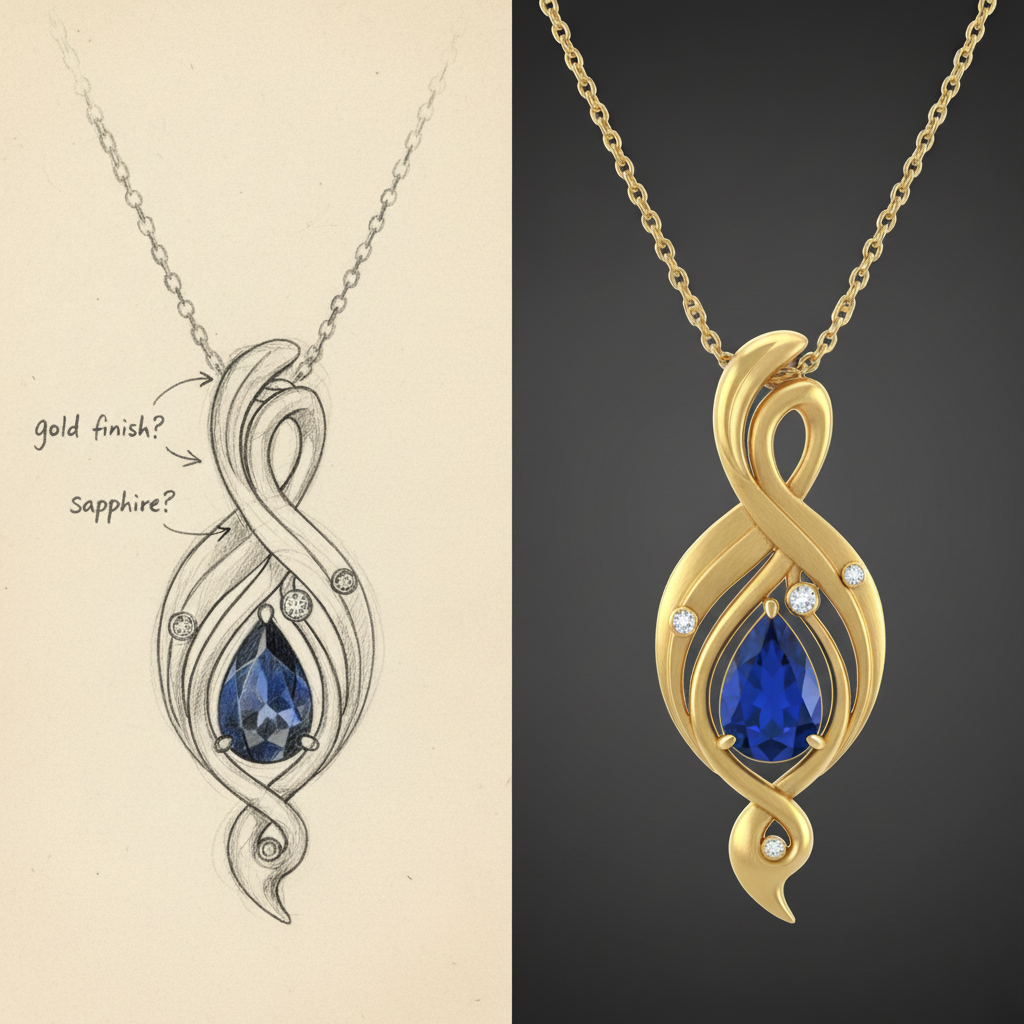

When you place hand sketching and CAD side-by-side, you see two powerful but different approaches to the design process. Traditional methods excel in creative exploration, while CAD provides the technical precision needed for flawless product design. The right choice often depends on what stage of the project you are in.
Neither method wins in every category. Instead, understanding their individual strengths helps you decide which tool to use and when. The following comparison highlights where each one shines, from initial cost to final accuracy.
Looking at a direct comparison helps clarify the roles of each method in product design. While CAD software minimizes human error, traditional methods allow for a level of artistic freedom that digital tools can sometimes restrict.
| Feature | Hand Sketching | CAD Software |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Low; it relies on the artist’s skill and is prone to human error. | High: allows for exact measurements and symmetry. |
| Speed | Fast for initial ideas; slow for detailed revisions. | Slower for initial setup; very fast for modifications. |
| Cost | Very low; requires only basic drawing supplies. | High; involves software licenses and hardware. |
| Flexibility | Excellent for exploring new ideas and creative concepts. | Excellent for technical changes and iterations. |
| Collaboration | Harder to share and requires physical copies. | Easy to share digitally for feedback and production. |
Thinking about this comparison raises a key point: can these methods be combined? Absolutely. The most effective design process often starts with a hand sketch to capture the creative vision. That concept is then imported or recreated in CAD software for refinement, precision adjustments, and preparation for manufacturing. This hybrid approach gives you the best of both worlds.
FAQs
When Is Traditional Hand Sketching Still the Better Choice?
Traditional hand sketching is the better choice during the initial brainstorming phase of the design process. It is ideal for quickly exploring new ideas, expressing creative concepts, and developing a core vision without being constrained by technical software. Its freedom is perfect for pure, unfiltered creativity.
Can Designers Combine Hand Sketching and CAD for the Best Results?
Yes, designers can and often do combine both methods for the best results. A common workflow involves using traditional methods to create initial concepts and then moving to CAD software for technical refinement, precise modifications, and creating production-ready files. This hybrid approach leverages the strengths of each tool.
Is CAD More Important to Learn Than Hand Sketching for Jewelry Careers?
For a modern jewelry career, both skills are highly valuable. CAD software is essential for precision manufacturing and is a non-negotiable part of the product design workflow. However, sketching remains a fundamental skill for creativity and client communication. A designer proficient in both is best equipped for the future of design.

